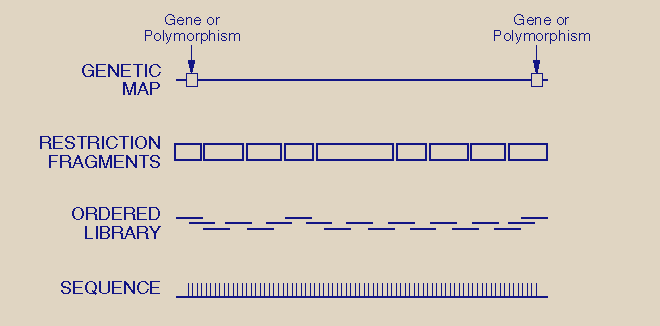
Fig. 10. Types of Genome Maps.
At the coarsest resolution, the genetic map measures recombination frequency between linked markers (genes or polymorphisms). At the next resolution level, restriction fragments of 1 to 2 Mb can be separated and mapped. Ordered libraries of cosmids and YACs have insert sizes from 40 to 400 kb. The base sequence is the ultimate physical map. Chromosomal mapping (not shown) locates genetic sites in relation to bands on chromosomes (estimated resolution of 5_Mb); new in situ hybridization techniques can place loci 100 kb apart. This direct strategy links the other four mapping approaches. [Source: see Fig. 9.]